18.2.2021
PROPERTIES
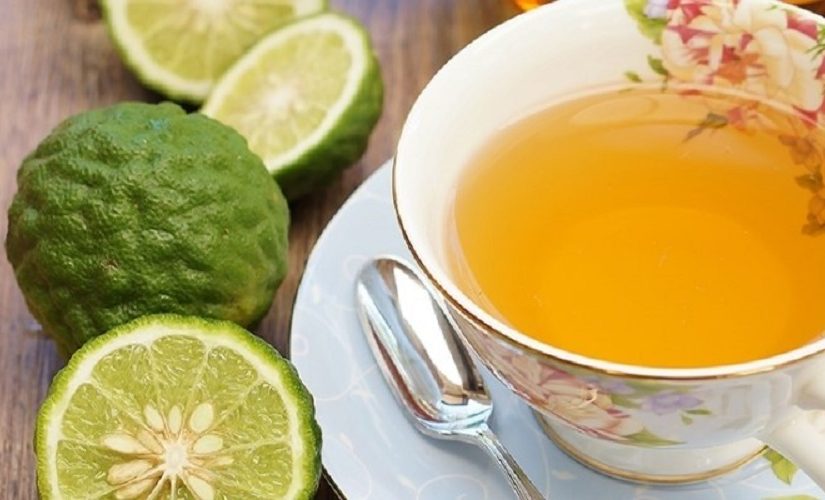
Bergamot could be the weapon capable of inhibiting the coronavirus. Bergamot is full of vitamin C and flavonoids that make it an excellent cholesterol lowering agent and an antibacterial potentially capable of inhibiting Covid-19, according to a recent study from the universities of Milan and Genoa.
In the past, the research of the University La Sapienza in Rome, carried out in collaboration with the Universities “Vita-Salute” of Genoa and “San Raffaele” of Milan, shed light on the potential of Naringenin, which would be able to inhibit infectious process of Covid-19.

MARKET AND HISTORY
In Italian houses, 3,000 tons of bergamots are transformed per year into juice, jams, honey, hydro-alcoholic gels, but above all into essential oil. This small green citrus fruit with powerful properties is the object of a juicy business in southern Italy: 90% of its production comes solely from the hills of Calabria. Like the lemon tree, bergamot comes from a cross-made from bitter orange. The Arabs who long occupied Calabria in the middle Ages could have imported it.
A NEW PERSPECTIVE AGAINST COVID-19
The intuition was born in the laboratory of the Unit of Histology and Medical Embryology of Antonio Filippini, at the Roman University: it was thought that the proliferation of the coronavirus could be prevented by inhibiting a specific molecular target responsible for the progression of the virus as soon as it enters the cell. Currently, the study is in the verification phase and the results of the first tests seem to confirm the original intuition of the Italian researchers.
Naringenin, as the Italian Society of Pharmacology explains, is a compound of the flavonoid family, which is commonly found in plants. It has antioxidant and immune system modulating activity, is found in large amounts in grapefruit, bergamot and, to a lesser extent in lemon, oranges and tangerines. Above all, naringenin, the very molecule at the center of the anti-Covid-19 scientific study, derived from the polyphenol contained in bergamot juice, in addition to the “anti-cholesterol” activity which has just been seen, increases the uptake of glucose in the muscles and the liver, therefore it helps to lower blood sugar and improve insulin activity.
The one against the Coronavirus is only the last frontier on the benefits of bergamot on health. There are, in fact, several scientific studies, which show how the flavonoids contained in bergamot have an action very similar to that of synthetic statins, that is to say, they block the enzymes of cholesterol synthesis.

In fact, other studies then show how the use of bergamot juice also helps lower the levels of LDL, “bad” cholesterol, and increase the levels of HDL, “good” cholesterol.
Bergamot, given the high content of vitamins C, B1, B2, which improve iron absorption, is useful in supporting therapy for anemia. Green gold from Calabria is an excellent appetite stimulant and, due to its high content of critical acid, is effective against intestinal parasites.
Finally, the antioxidant properties of bergamot juice increase the activity of enzymes with antioxidant action, limit the production of free radicals on the walls of blood vessels and neutralize inflammatory mechanisms.





