3.11.2019
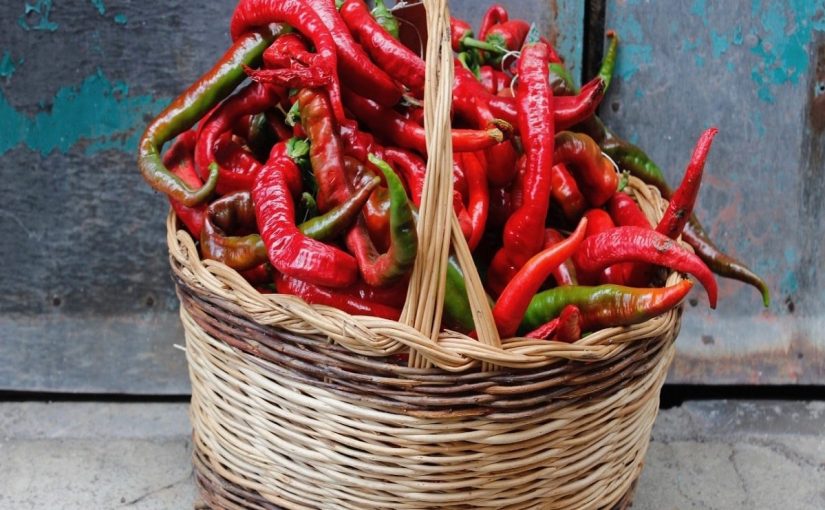
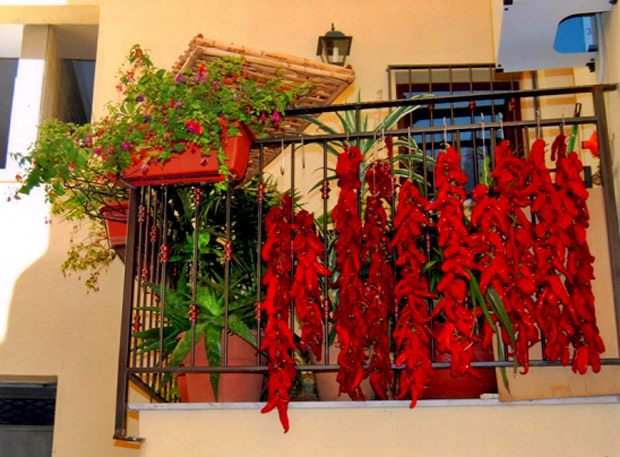
Discovering the Zafarana or those red peppers, sweet and not at all spicy, with the characteristic shape of a goat’s horn, which once dried and cooked, have the peculiarity of being crispy. It is the tastiest fruit of summer vegetables.
Perhaps some will know the Senise peppers, others the Roggian peppers in the province of Cosenza. But still few know of the existence of Zafarana di Tortora, the first town in north-western Calabria, on the border with Basilicata. Here, for years, the youngest tell, the grandmothers baked “nzerte of zaferana” (wreaths of peppers) when they made bread, to then obtain the powder for use in the kitchen. Those same grandmothers who today look at their astonished grandchildren who return to their country just to cultivate zaferana, like some agronomists come from abroad. Because yes, in Tortora that much-vaunted return to youth farming is anything but a chimera or an illusion. It’s all true, with real names and faces and with a precise purpose: to enhance the Zafarana of Tortora.

FROM BRAZIL TO CALABRIA
Both that of Senise, that of Roggiano Gravina and Tortora peppers are part of the same family, or of those red peppers, sweet and not at all spicy, with the characteristic shape of a goat’s horn, which once dried and cooked, for their peculiarity of being crunchy, are justly called “cruschi” (crispy). Originating in Brazil, they are known in Italy and Calabria after the discovery of America and find their ideal habitat in the mild climate between Calabria and Basilicata, in that special soil of the most hilly areas.
Among the three tipology of peppers (Senise, Roggian and Tortora) there is no competition, on the contrary: there is a constructive relationship of collaboration and mutual support, all the farmers are aimed at making the world know about a product that is still so little known.
THE SAFFRON OF THE POOR
What differentiates the Zafarana from Tortora is that, having a slightly thinner skin, it tends to have less water stagnation and therefore lend itself more to drying. The name obviously brings us back to saffron: it derives from the same Arabic root of zafran, because the red color of the powdered zafarana is reminiscent of that of the crocus sativus. The latter is the well-known species of flowering plant of the Crocus genus in the iris family Iridaceae, famous for producing the spice saffron, from the filaments that grow inside the flower.
In reality, however, it is a very different product in terms of taste and cost, this is why it has been nicknamed “the saffron of the poor” because it is always present on the Tortorese tables. Here, in fact, every family has cultivated its zafarana since ancient times, so much so that in a church of the town a fresco of 1628 was found where it is depicted among eggplants and oranges.

The association La Zafarana di Tortora, with its president Giuseppe Limongi, a professional ceramist, tries to protect such an ancient product and to ensure that it remains a very small niche production. He told: “I am a deep lover of art and nature, and zaferana is nothing but a wonderful form of art present in nature“.
A LONG AND COMPLEX CULTIVATION
Tradition has it that the production of zaferana begins in March, during the week of Saint Joseph. Later, in April, when the seedlings are born, they are put in a seedbed until June; then the best are selected and planted in the fields between June and July. Harvesting can begin in August and also end in December depending on the weather.
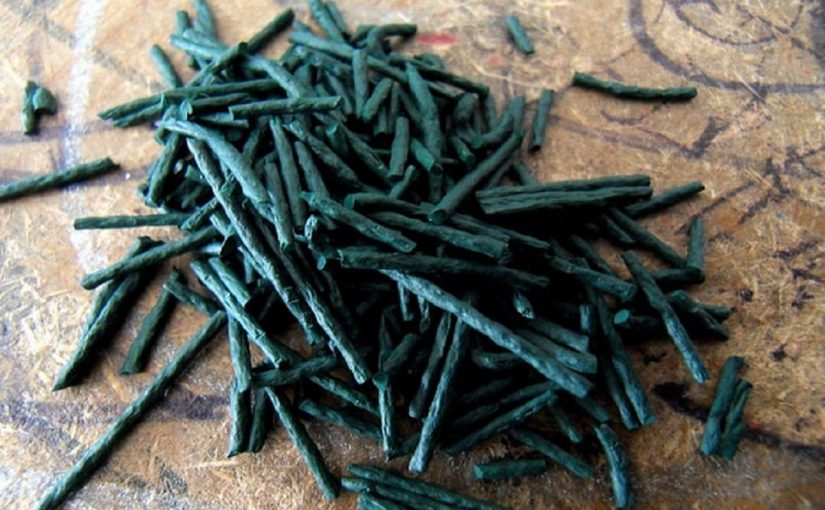
Finally, once collected, they are twisted making a small hole with a needle one behind the other in the typical “nzerte” (wreaths ), or those braids of peppers that you see hanging in the houses, at the windows, on the balconies. The important thing is that they are ventilated and dry places, not exposed to the sun, but always in the shade and without humidity. So that they can last for months, even a year.
Then it can be eaten either fried (cooking lasts for a few seconds) in a pan, or in powder.
THE ZAFARANA IN THE KITCHEN
The typical way to cook zafarana is to use the powder (so called “pisata“) for cooking bolied potatoes (the plate is called “patane cca zaferana pisata“). The powder is also associated to consumption of oil, garlic and salt, paired with bread, eggs or dried figs.
Today the peppers are used in many ways in the kitchen, but the most recommended is to taste them alone, fried in a pan. The second one can instead try the classic combination with cod, just as you traditionally eat the Senise pepper in Basilicata.
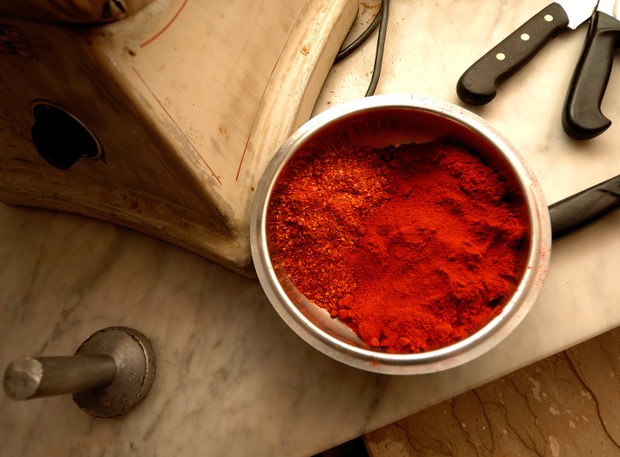

Once powdered, however, one of the most traditional combinations is to sprinkle it over pasta such as lagane and chickpeas or spaghetti with garlic and oil, but also directly into fusilli or tagliatelle.
Alternatively, zaferana can also be added during the preparation of bread or biscuits. Also perfect on the second course: on the fried egg, on the meat with a drizzle of oil, or on the fish, since it also favors conservation.
Finally, why not try a nice risotto made exclusively with zafarana?
ZAFARANAFEST
To taste the zafarana in all its forms, it is worthwhile going to the party that the association La Zafarana di Tortora has been organizing for ten years every first weekend of October, at the end of the harvest.
This is also the right occasion to learn a lot about this product: In addition to food and goliardic aspects, much importance is given to cultural aspects, with conferences on the benefits of zaferana, with interesting projects with schools and so on.
Further, this is also an opportunity to visit the town of Tortora, with a truly enviable historic center, like the nearby and delicious village of “Aieta“.